Innerlife STS Clinical Supervision Study
The Innerlife STS System was recently used to complete a study on Clinical Supervisions. The results of the study were presented at the 2014 APA annual convention in Hawaii. The study was conducted at The Gronowski Center, Palo Alto University, Palo Alto, California
The Innerlife STS System is a cloud-based platform for Treatment Reports, Analytics, Outcome Tracking, and Documentation for mental health care. Innerlife STS creates and composes conceptualized narratives and builds them into professional-grade reports. These reports are designed for use by primary care physicians, mental health clinicians, and justice system professionals and include Mental Health Assessment Reports, Mental Health Treatment Reports, and Forensic Evaluation Reports.
The study included 8 Evidence-Based Principles in Supervision Trainings. The following represents preliminary findings from the first subjects (therapists, supervisors, and clients) in the study. Participants were:
- Professor Larry E. Beutler, Ph.D., Principal Investigator
- Satoko Kimpara, Ph.D., Project Director
- Nancy Haug, Ph.D.
- Sandra Macias, Ph.D.
- Nichole Shiloff, Ph.D.,
- Peter Goldblum, Ph.D.
- Rainey Sealey Temkin, M.A.
The gap between what is taught inside the classrooms of research faculty and what is experienced in clinical supervision is a frequent concern of both psychology accrediting bodies and students themselves.
Programs which value the use of Evidence-Based Psychotherapies often find it difficult to ensure that therapist trainees are providing optimal treatments, given there are more than 150 “empirically effective” treatments.
Beutler et al. (1990, 2000, 2006) established empirically derived principles (i.e., Systematic Treatment Selection; STS) to guide the therapeutic work, cut across therapeutic models, and allow diverse groups of psychotherapists to describe and apply their methods through a common language.
In the current study, we constructed a model designed to facilitate supervision through teaching and illustrating principles of effective change in the supervisory process.
The purpose of this preliminary study is: 1) to assess satisfaction of supervision trainings for supervisors and student therapists; 2) to determine study feasibility and; 3) to pilot procedures for a larger efficacy study in a psychology training clinic serving community mental health clients.
Impairment Level Principle
Relationship Principles
Resistance Principles
Coping Style Principles
Readiness Principle
8. Clients who are in more advanced stages of readiness for change (e.g., preparation, action, maintenance) are more likely to improve in psychotherapy than those at lower stages of readiness (pre-contemplation, contemplation).
Procedure
- Participants who signed consent included: student trainees (n=43), supervisors (n=10), and clients (n=18) for 8 weeks. The final numbers reported here include: 25 student trainees, 6 supervisors and 18 clients (7-completed the study, 9-on going, and 2 attrition -1 client and 1 supervisor).
- Prior to recruiting clients, supervisors and students were trained on eight evidence-based principles, all of which have produced strong evidence associated with effective treatment (Norcross, 2011).
- Supervisors received 8 sessions of training and students received 2 sessions. Learning evaluations, completed by students and supervisors post-training, were used to assess the effectiveness of the trainings (see Table 1).
- The Outcomes Questionnaire-45 (Lambert & Burlingame, 1996) was used to assess client progress over the 8-week study period (Figure 1), during which supervisors and student therapists implemented STS.
- Study feasibility was captured through an evaluation designed to assess student therapist feedback after study completion (see Table 2).
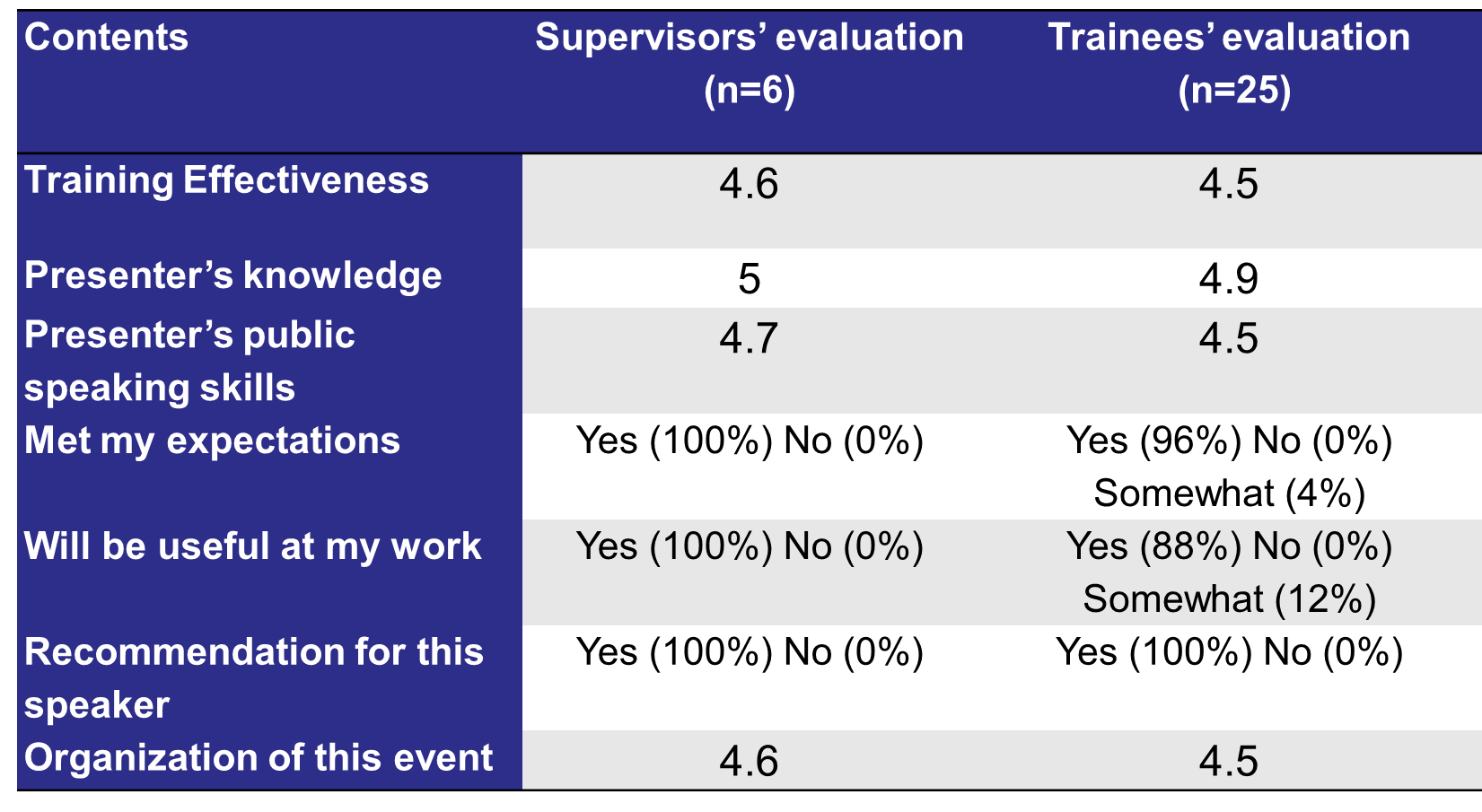
Table 1. Post-Training Satisfaction Survey
(1 = Poor, 2 = Fair, 3 = Good, 4= Very good, 5= Excellent)
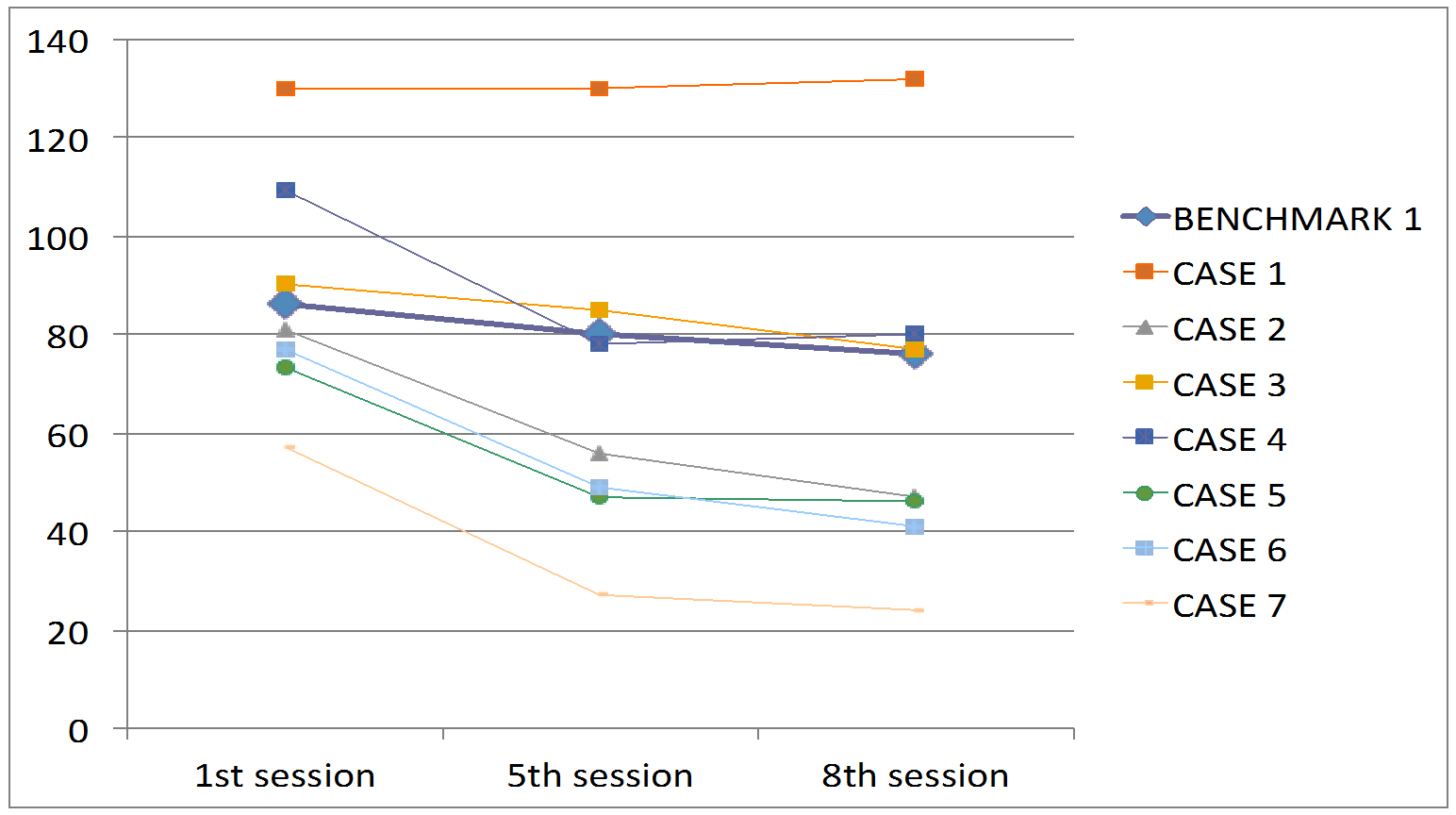
Figure 1. OQ-45 Client Scores
Results are based on benchmarking observed pre-post effect size estimates against treatment efficacy (see Minami et al. 2009). Six of 7 cases demonstrated large effect size estimates (d=.96-1.15) through session 8. Case 1 was a client with a long-standing schizophrenia diagnosis. (n=7)

Table 2. Post-Study Evaluation
(n=13)
Conclusions
• Student feedback indicated that evidence-based supervision helped with case conceptualization, addressing client resistance, selecting treatments based on internalizing and externalizing factors, a clearer sense of diagnostic and treatment interventions, treatment flexibility based on specific client characteristics, and valuable assessment information that may have otherwise been missed in initial interview.
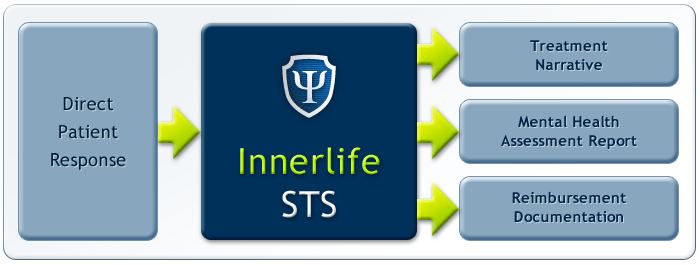
Innerlife STS:
- Supports the clinician's thinking about how best to prescribe mental health treatment for a particular patient
- Automatically generates a mental health assessment and treatment narrative
- Automatically generates the Patient Psychological Evaluation designed for use by judges, lawyers, and the entire law enforcement system
- Automatically generates the complete documentation package necessary for reimbursement by insurance companies and government-sponsored health programs
- Tracks treatment outcomes over the full treatment lifetime of clients
- Stores historical assessment reports and outcomes to fully support audits


